Many users currently using WordPress want to explore Joomla as an alternative for web design projects. Here are some key points to help you transition smoothly from WordPress to Joomla.
Differences in Usage Between WordPress and Joomla
WordPress users typically install themes and plugins to build their websites and solve issues by searching for and adding new plugins or themes. When transitioning to Joomla, many users tend to skip documentation and use Joomla in a similar way—by looking for templates and plugins without understanding its core structure.
You might think that Joomla templates work like WordPress themes or that Joomla plugins function like WordPress plugins—but they don't. If you use Joomla as if it were WordPress, you may run into difficulties.
To help you get started, the following sections outline key structural differences in Joomla. It’s highly recommended to go through hands-on exercises like a beginner to learn Joomla the right way.
Joomla Template vs. WordPress Theme
In WordPress, themes come fully equipped with features like content retrieval, display settings, banner management, and sidebar widgets. Simply installing a theme often results in a fully functional website.
Joomla templates, however, focus primarily on layout and styling. They provide predefined layouts and CSS styles but do not handle data processing. After installing and activating a Joomla template, you may see a blank page or just a few elements. This is normal—Joomla's modular approach allows you to transform a website using only one or two templates.
Since Joomla separates layout and functionality, you can switch templates without affecting content or features. This flexibility allows for easy design changes without disrupting site operations.
Joomla Module vs. WordPress Widget/Block
Both Joomla Modules and WordPress Widgets/Blocks are used to create additional content areas, such as side banners or news sections.
In Joomla, Modules are an essential part of building web pages. Unlike WordPress, where users often modify themes directly, Joomla users frequently manage layouts through the Module Manager.
Many users overlook the powerful customization options of Joomla Modules. To better understand them, try the Joomla 5 Practice 01 tutorial, which covers installing a demo site, using XiroAdmin, and adding text, images, and banners via Modules. Advanced lessons will explore even more useful Module features.
Displaying Modules on Specific Pages (Menu Item URL)
Joomla allows you to assign Modules to specific pages (Menu Item URLs).
Examples:
- Display news modules only on the homepage.
- Show Product A’s banner on pages X and Y, and Product B’s banner on page Z.
- Add special article recommendations on pages X and Z.
This feature provides fine-grained control over content placement, allowing you to display or hide elements as needed.
Module Access - Controlling Visibility Based on User Access Levels
Joomla has built-in User Access Levels:
- Public: Visible to all visitors.
- Guest: Visible only to non-logged-in users.
- Registered: Visible only to logged-in users in the "Registered" group.
- Special: Visible to users with higher privileges (e.g., site moderators).
- Super Users: Full access to all content and settings.
Example Use Case:
- If you want to display a "Sign Up" message only to non-logged-in users, set the Module's access to Guest. This prevents it from appearing for users who are already registered.
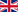
Joomla’s Powerful URL Customization with Menu Items
In WordPress, URLs are managed using permalinks with limited customization options. In Joomla, every component can have a unique, fully customizable URL.
To optimize for SEO, follow the tutorials on enabling SEF URLs and structuring custom URL paths.
Example Use Case:
- Convert an article’s URL to
/about-companyfor better readability. - Assign a different template to a specific menu item and customize its settings independently.
Joomla Plugin vs. WordPress Plugin
In WordPress, almost every functionality is implemented through plugins, making them central to site customization.
In Joomla, Plugins work differently. They act as processing units that modify or extend core system functionalities. Joomla Plugins often receive raw data, process it, and return the modified data to the main system.
So what is the equivalent of WordPress Plugins in Joomla?
Joomla Extensions, which include Components, Modules, and Packages. While the naming is different, the installation and usage process is just as straightforward as WordPress plugins.
Getting Started with Joomla 5
To effectively learn Joomla 5, follow the "Joomla 5 Web Development Practice" series. These tutorials are designed for beginners with no prior web development experience, covering everything from the basics to advanced techniques.
List Tutorial Joomla 5

This guide walks you through each step of installing Joomla 5 on a domain that is already pointed...
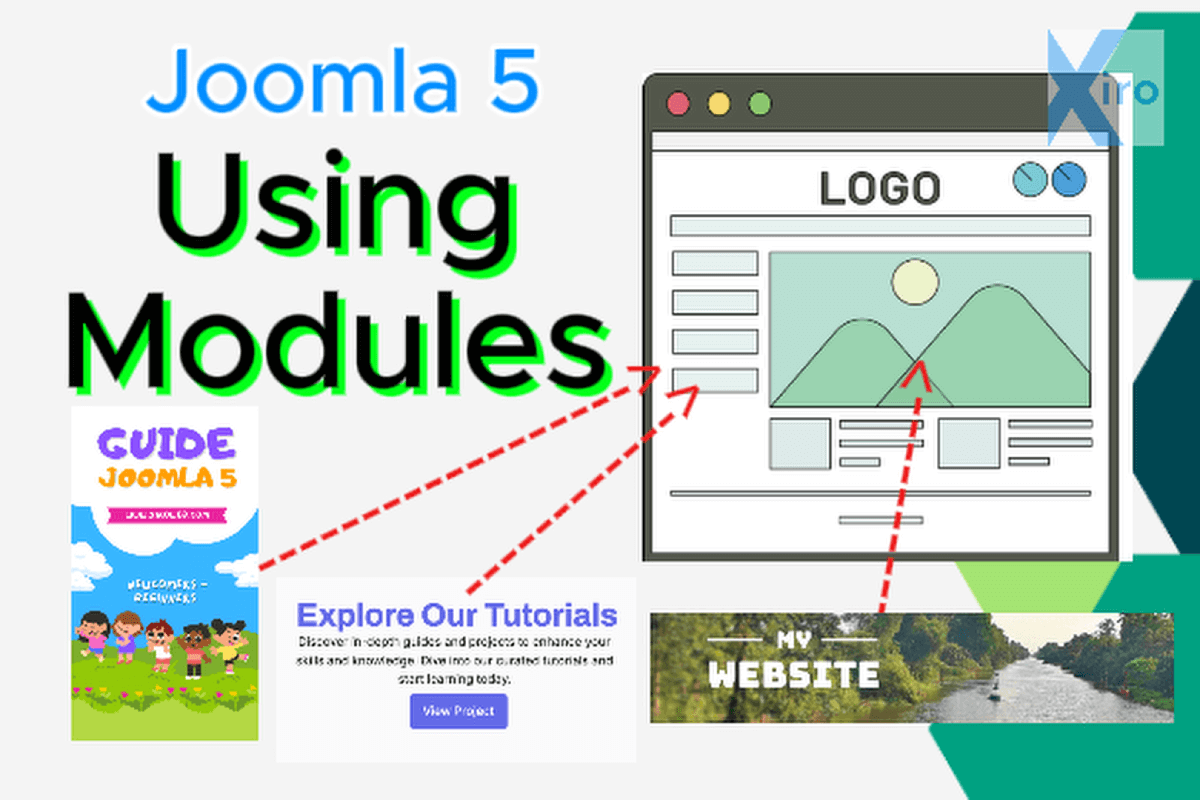
This Practice Lesson a step-by-step guide on how to use modules in Joomla 5, specifically designed...

In this practice lesson, we will continue exploring how to use Joomla 5 Modules effectively so you...
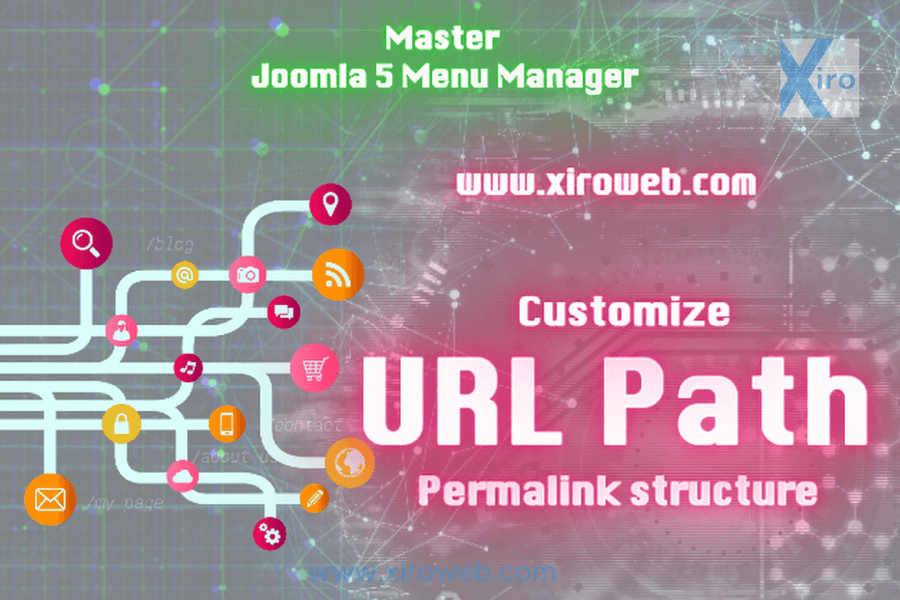
Joomla Menus are a powerful, unique, and essential system that helps you define the entire URL...
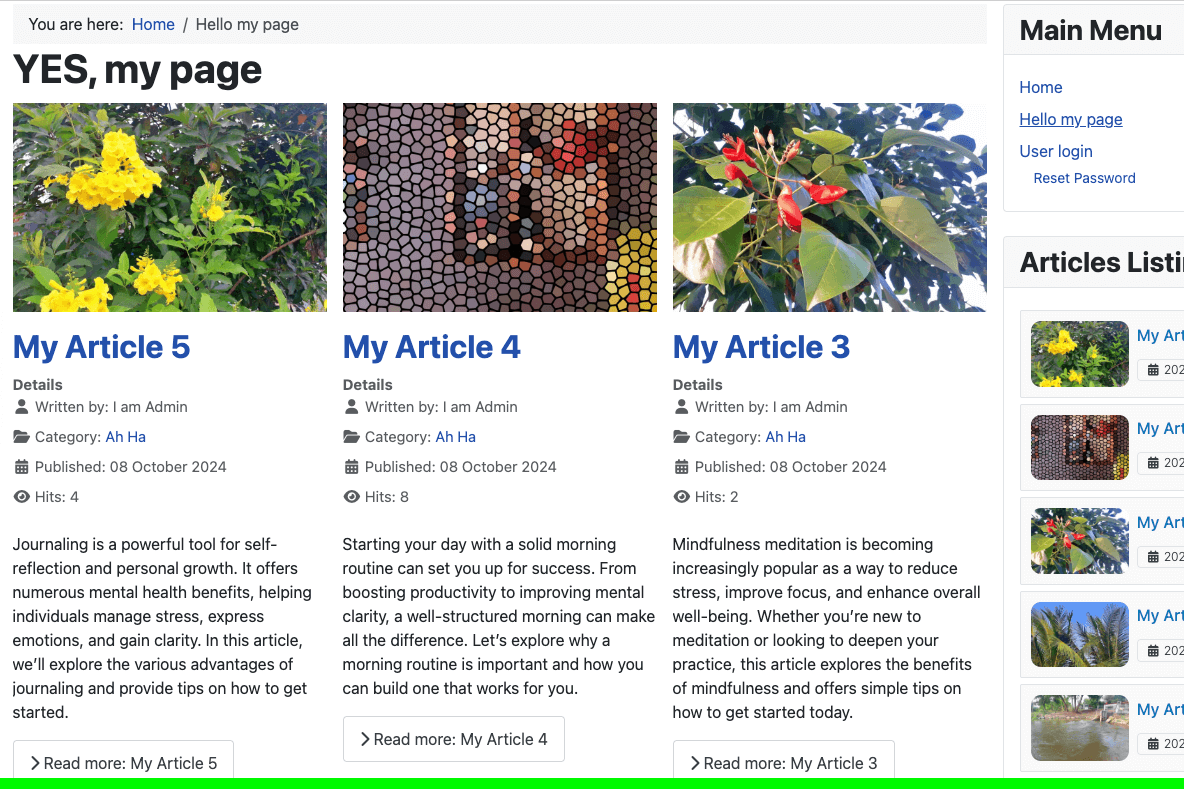
In this practice, you will learn how to create Articles and Categories. Don’t skip this lesson, as...
Content written by Dustin Dũng - Xiroweb

Dustin Dzung with 15 years of experience in using and developing websites with Joomla!, from the first version of Mambo to Joomla! 1.0 and up to the present Joomla! 5.x.